Synaptic plasticity underlying action control in physiological and pathological conditions
In everyday life, we use two strategies to control our actions: the flexible goal-directed action strategy and the habitual stimulus-driven action strategy. These two types of actions are encoded by discrete brain regions: the caudate nucleus (dorsomedial striatum in rodents) and putamen (dorsolateral striatum in rodents), respectively. We are interested in deciphering the synaptic plasticity in respective regions underlying these actions in physiological and pathological conditions using brain slice patch-clamp electrophysiological recording, animal behavioural training, transgenic manipulation, photogenetics, and chemogenetics interference techniques.





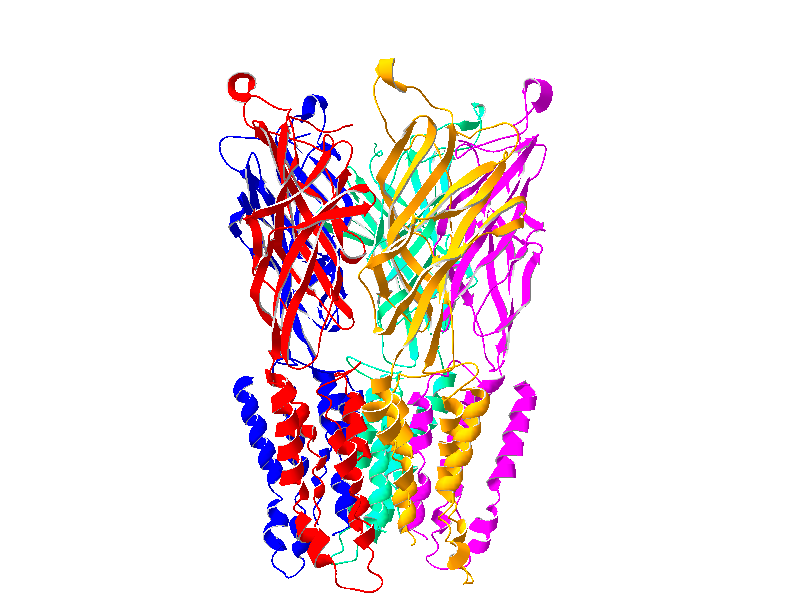
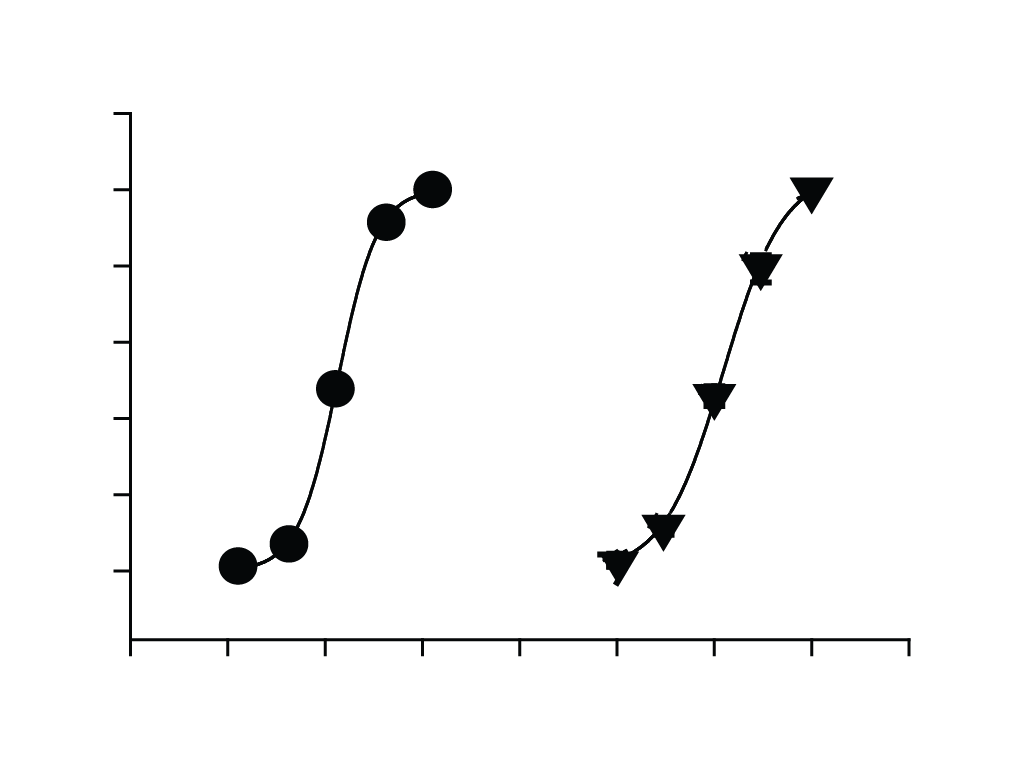
Structure and function of glycine and GABAA receptors
The glycine and GABAA receptors belong to the Cys-loop ligand-gated ion channels superfamily, which also includes the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor and the 5-HT3 receptor (5HT3R). All members of this superfamily are widely-used drug targets in many neurological and psychiatric diseases. We are interested in determining their structure and function relationships using molecular biology manipulation, whole-cell patch-clamp electrophysiological recording, and voltage-clamp fluorometry techniques.